The following topic applies to
Xcode*.
A single project can contain multiple targets; the currently active target determines how your project is built. This topic describes how to build the target using the Xcode* IDE and also documents the build steps using the xcodebuild command line utility.
Building using the Xcode* IDE
Select the target to be built in the project editor under Targets.
Select Product > Build.
To view the results of your build, click the Log Navigator (
 ) button.
) button.
You can change the compilation order of the files in an Xcode* target. This may be necessary to compile Fortran source files that define modules (producing .MOD files). These can, in turn, be used by Fortran sources that use the modules. To re-order the files listed under a target's Compile Sources, click a source file and drag it before or after other compilations.
Note
Xcode* 4.6 is the last major Xcode* release that includes the llvm-gcc compiler and the GDB debugger. Please plan to use the LLVM CLANG Compiler and LLDB debugger in future releases.
Building from the Command Line Using the xcodebuild Utility
You can also use the xcodebuild utility to build a target. This utility uses the Xcode* project settings to build target projects from the command line. If you have previously configured your Xcode* project to build with the Intel compiler, xcodebuild invokes it from the command line.
Note
Starting with Xcode* version 4.3, you must manually download and install the Xcode* command-line tools.
See the Xcode* documentation for details.
To build from the command line:
Check that the Xcode* project is configured to use the Intel® Fortran Compiler.
Launch a terminal window from the Finder by selecting Applications > Utilities > Terminal .
Change directories to the directory containing the Xcode* project file (.xcodeproj).
If you have multiple versions of Xcode*, use the xcode-select utility to verify the current Xcode* version.
Issue an xcodebuild command. For example:
xcodebuild -project HelloWorld.xcodeproj -target HelloWorld -configuration Debug
Run the program built in the example from the previous step by entering the following:
./build/Debug/HelloWorld
For more information, refer to the xcodebuild man page.
Setting the Executable's Architecture
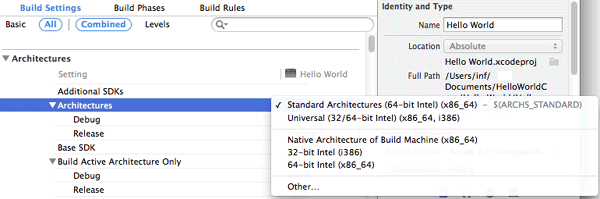
Before building a 64-bit executable from within Xcode*, you may need to edit the executable's target architecture. To change the Architectures setting:
Click the target you want to change in the project editor under Targets and select the Build Settings tab.
Under Architectures, select the desired architecture.
Note
The Intel® Fortran Compiler generates code solely for Intel® architectures.
Building Universal Binaries
You can build universal binaries, which operate on both IA-32 and Intel® 64 architectures. If you select more than one architecture in your build configuration, a universal binary containing the executables for all the selected architectures is created.
For example, for the Release configuration, if you set the architecture property to the value Standard (32/64-bit Intel), then binaries for both the IA-32 and Intel® 64 architectures are created and put into the executable.