The following applies to Microsoft
Visual Studio* 2012 and 2010.
Remote debugging lets you use your local (host) system to debug an application running on a remote system.
Remote Debugging using Visual Studio*
There are two remote connection types available: DCOM ( "Remote with Windows authentication") and TCP/IP ("Remote with no authentication"). For more information on initial setup for remote debugging, refer to the Visual Studio* remote debugging setup topics in the Microsoft* MSDN documentation.
Remote debugging typically requires use of the debugging monitor (msvsmon.exe). Run the monitor in the correct mode for the remote system's architecture. To do this, on the remote system, select the program group Microsoft Visual Studio 2012 (or applicable version year), then choose Visual Studio Tools and select the correct Remote Debugger Folder.
Remote debugging also requires proper set up of the IDE Debugging property page on the host machine.
To set up remote debugging using the IDE property pages:
On the host machine, choose Project > Properties > Configuration Properties > Debugging. Your screen should resemble the following:
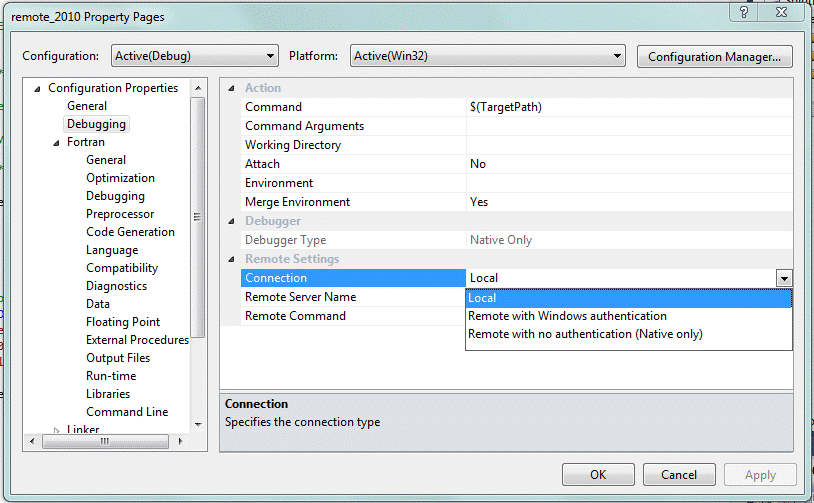
Specify the following:
Connection: Use the drop-down box to select the type of connection.
Remote Server Name: Use the drop-down box to select the name of the remote system.
Remote Command: Type the command you want to issue on the remote machine. Typically, this is a pathname to an executable file (.exe) on the remote machine; for example: d:\remote\myapp.exe
Optionally, set Attach to "Yes" to attach to an application that is already running on the remote machine.
To start remote debugging:
Make sure you have the necessary remote debugging permissions on the remote machine. For example, you need Administrator privileges if you want to debug a process running on a remote machine under another account name.
Run the Remote Debugging Monitor on the remote machine.
Launch Visual Studio* on the host machine and use it to attach to a program you want to debug on the remote machine, or launch a program you want to debug on the remote machine.